Usage¶
Using the Debugbar¶
When the Debugbar is enabled, the Debugbar is shown on the bottom of the screen, similar to the documentation preview.
Based on your configuration, it shows the Collectors for the current request. You can open, close, restore or minimize the toolbar for your need. The state will be remembered.
Debugbar Facade¶
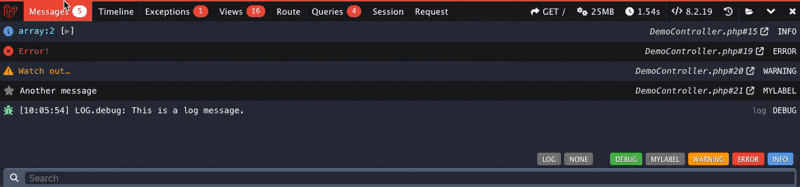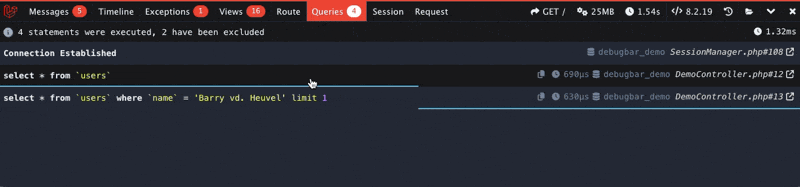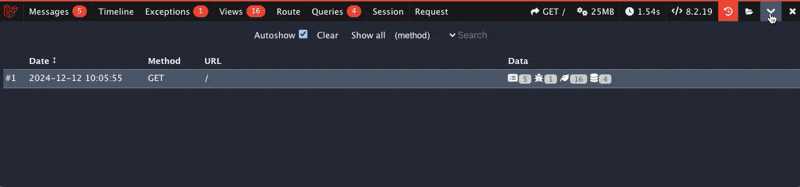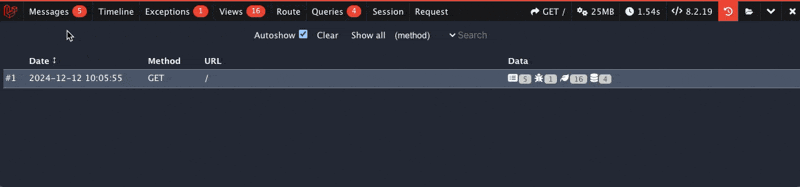
You can now add messages using the Facade (when added), using the PSR-3 levels (debug, info, notice, warning, error, critical, alert, emergency):
Debugbar::info($object);
Debugbar::error('Error!');
Debugbar::warning('Watch out…');
Debugbar::addMessage('Another message', 'mylabel');
And start/stop timing:
Debugbar::startMeasure('render','Time for rendering');
Debugbar::stopMeasure('render');
Debugbar::addMeasure('now', LARAVEL_START, microtime(true));
Debugbar::measure('My long operation', function() {
// Do something…
});
Or log exceptions:
Helpers¶
There are also helper functions available for the most common calls:
// All arguments will be dumped as a debug message
debug($var1, $someString, $intValue, $object);
// `$collection->debug()` will return the collection and dump it as a debug message. Like `$collection->dump()`
collect([$var1, $someString])->debug();
start_measure('render','Time for rendering');
stop_measure('render');
add_measure('now', LARAVEL_START, microtime(true));
measure('My long operation', function() {
// Do something…
});
If you want you can add your own DataCollectors, through the Container or the Facade:
Debugbar::addCollector(new DebugBar\DataCollector\MessagesCollector('my_messages'));
//Or via the App container:
$debugbar = App::make('debugbar');
$debugbar->addCollector(new DebugBar\DataCollector\MessagesCollector('my_messages'));
Enabling/Disabling on run time¶
You can enable or disable the debugbar during run time.
NB. Once enabled, the collectors are added (and could produce extra overhead), so if you want to use the debugbar in production, disable in the config and only enable when needed.
Storage¶
Debugbar remembers previous requests, which you can view using the Browse button on the right. This will only work if you enable debugbar.storage.open in the config.
Make sure you only do this on local development, because otherwise other people will be able to view previous requests.
In general, Debugbar should only be used locally or at least restricted by IP.
It's possible to pass a callback, which will receive the Request object, so you can determine access to the OpenHandler storage.
Twig Integration¶
Laravel Debugbar comes with two Twig Extensions. These are tested with rcrowe/TwigBridge 0.6.x
Add the following extensions to your TwigBridge config/extensions.php (or register the extensions manually)
'Barryvdh\Debugbar\Twig\Extension\Debug',
'Barryvdh\Debugbar\Twig\Extension\Dump',
'Barryvdh\Debugbar\Twig\Extension\Stopwatch',
The Dump extension will replace the dump function to output variables using the DataFormatter. The Debug extension adds a debug() function which passes variables to the Message Collector,
instead of showing it directly in the template. It dumps the arguments, or when empty; all context variables.
The Stopwatch extension adds a stopwatch tag similar to the one in Symfony/Silex Twigbridge.